Virtualization is a great way to do things such as try out new operating systems, test out software, or even test Windows updates before applying them to your “real” computer and so on. VMware Workstation is one of the better programs you can use to create virtual machines on your personal computer at home or even at the office.
When using VMware Workstation, you may want to transfer files between your VMware host computer and one of your virtual machines. To do so, you can usually enable the Guest Isolation feature for drag and drop so you can copy files from your host to your VM and vice versa. But sometimes this doesn’t work as designed, especially for VMs running the Linux OS. Fortunately, there is a secondary method you can use to do these file transfers. In this article, we will be showing you how to share files and folders between your hot and Linux VMs in VMware Workstation.
The first thing you need to do is enable Shared Folders in the settings for your Linux VM. To do so, go to the settings for the VM and then to the Options tab and then the Shared Folders section. Now you can set the folder sharing option to always enabled or enabled until the next power off or suspend. Next, you will need to choose a local folder on your VMware host that you want to share with the Linux virtual machine by clicking on the Add button.
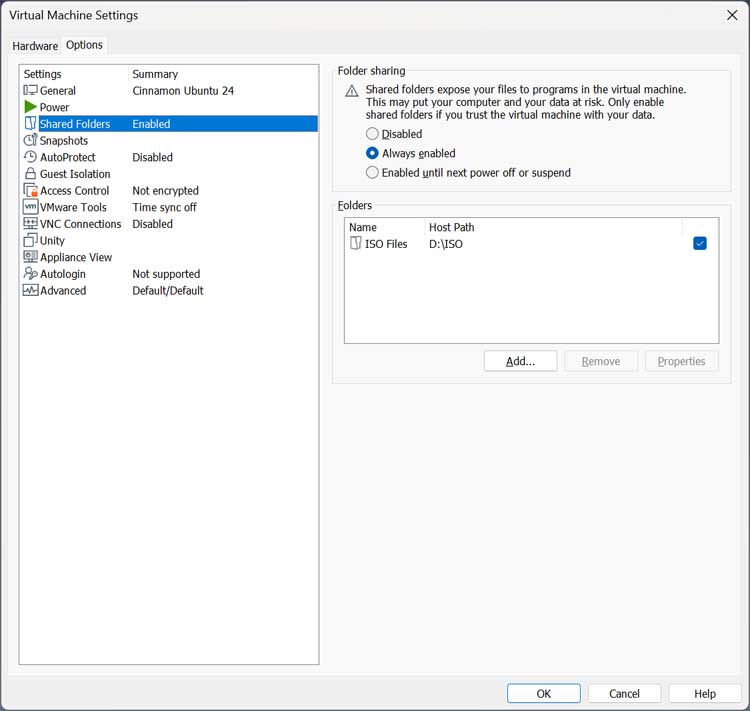
Once you have your VMware host configured with its shared folder, you will need to do a little configuration on your Linux virtual machine. First, you need to make sure VMware Tools are installed on the VM
You can do this via the terminal, but the command will vary depending on your version of Linux.
Ubuntu/Debian-based systems
sudo apt update
sudo apt install open-vm-tools open-vm-tools-desktop
RHEL/CentOS/Fedora systems
sudo dnf install open-vm-tools open-vm-tools-desktop
Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S open-vm-tools
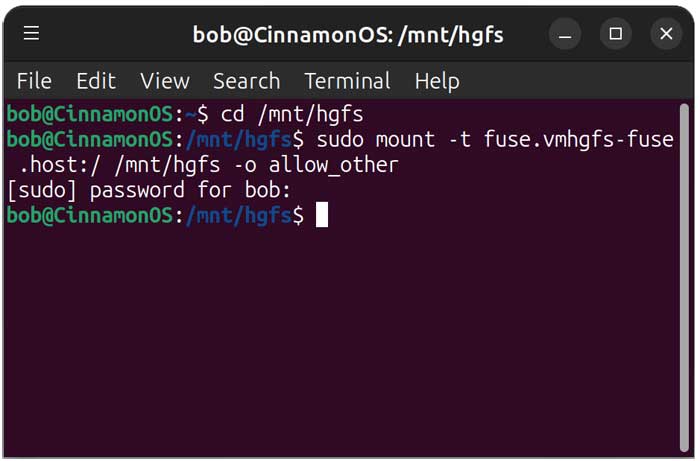
Next, we need to open a terminal and type cd /mnt/hgfs to see if the hgfs folder is there. The hgfs folder is a special directory used by VMware Tools inside a Linux virtual machine. It stands for Host–Guest File System and is the container VMware uses to store all shared folders
If the hgfs folder is not there, type – sudo mkdir -p /mnt/hgfs.
Then we will need to mount the shared folder using the sudo mount -t fuse.vmhgfs-fuse .host:/ /mnt/hgfs -o allow_other command. You will need to enter your admin password for this command.
Here is a breakdown of what each part of the command does.
sudo
Runs the command with root privileges (required for mounting).
mount
The Linux command to attach a filesystem to a directory.
-t fuse.vmhgfs-fuse
Specifies the filesystem type. fuse.vmhgfs-fuse is the VMware-specific FUSE driver that allows mounting shared folders from the host.
.host:/
This is the special VMware identifier for the host machine. It tells the VM to mount the shared folders provided by the host.
/mnt/hgfs
The mount point inside your VM where the shared folders will appear.
-o allow_other
This is an option for FUSE mounts that allows users other than root to access the mounted filesystem.
If you want to make the folder persistent (Optional), you can type .host:/ /mnt/hgfs fuse.vmhgfs-fuse defaults,allow_other 0 0.
You can then check the folder status by typing ls /mnt/hgfs. You can also browse to the folder in the Files app under /mnt/hgfs/share name.
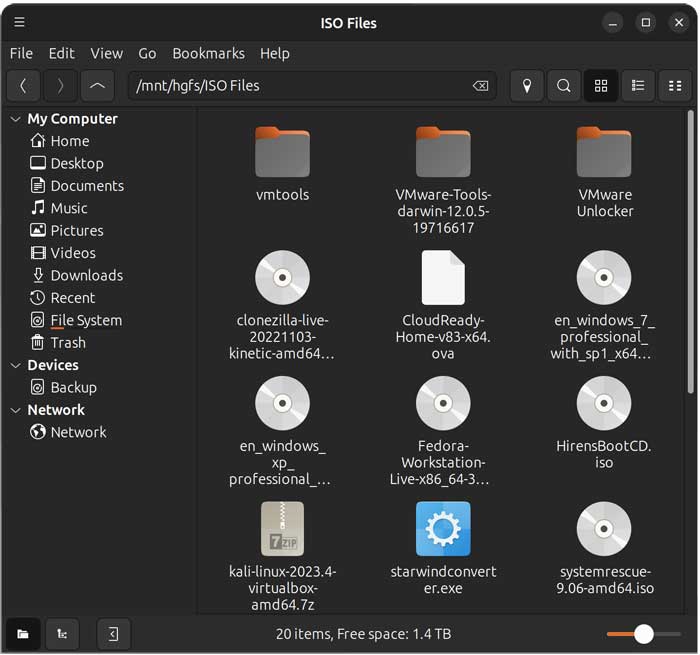
As you can see, our Linux folder matches the Windows folder on the VMware Workstation host.
If you want to unmount the folder from your Linux VM, you can use the sudo umount /mnt/hgfs command. Be careful when deleting or unmounting your folder in your Linux VM so you don’t accidentally delete the files in the shared folder on your VMware host. You may want to go back to the virtual machine’s settings and remove the shared folder first just to avoid any problems.
You can check out some of our other Linux tech videos here.
For additional training resources, check out our online IT training courses.
Check out our extensive IT book series.