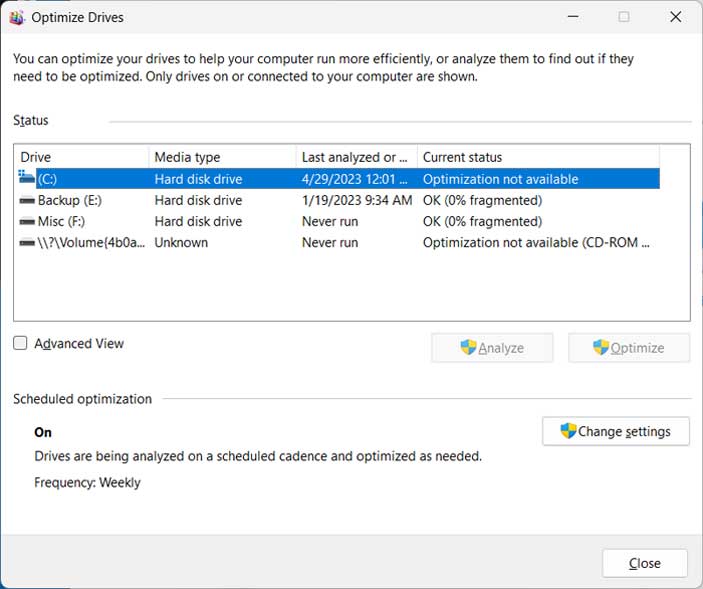
If you are the type who likes to keep their computer running in tip top shape, then you might occasionally check the optimization status of your hard drives. With newer versions of Windows, the operating system takes care of the hard drive defragmentation process so you don’t need to “defrag” it yourself.
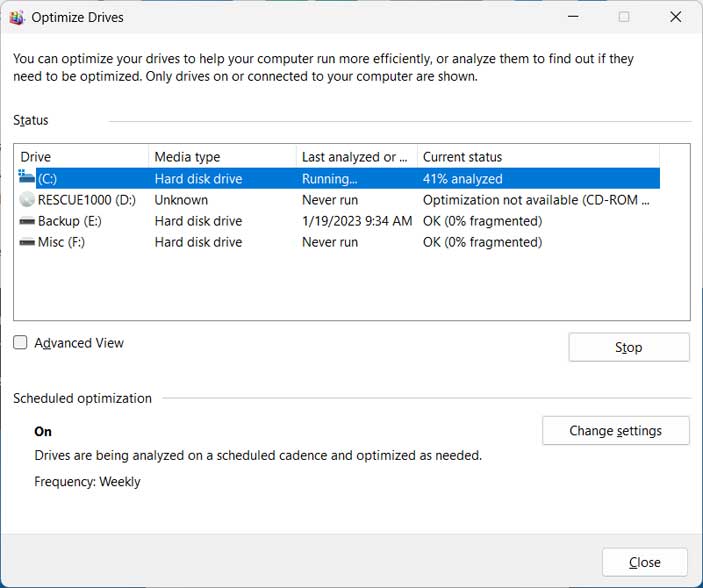
If you right click a drive, select Properties and then go to the Tools tab, will see a section labeled Optimize and defragment drive. Then if you click on the Optimize button, you will be able to see the optimization status for all of the drives on your computer. It also will show you when it was last analyzed or defragmented.
If you see a message under the Current status section that says Optimization not available, it might be because the dirty bit is set on that particular drive. The dirty bit can get set on a drive when the file system is in an inconsistent state from things such as the volume having outstanding changes or changes were made to the volume and not applied before the computer was shut down. In this article, we will be showing you how to reset the hard disk dirty bit in Windows.
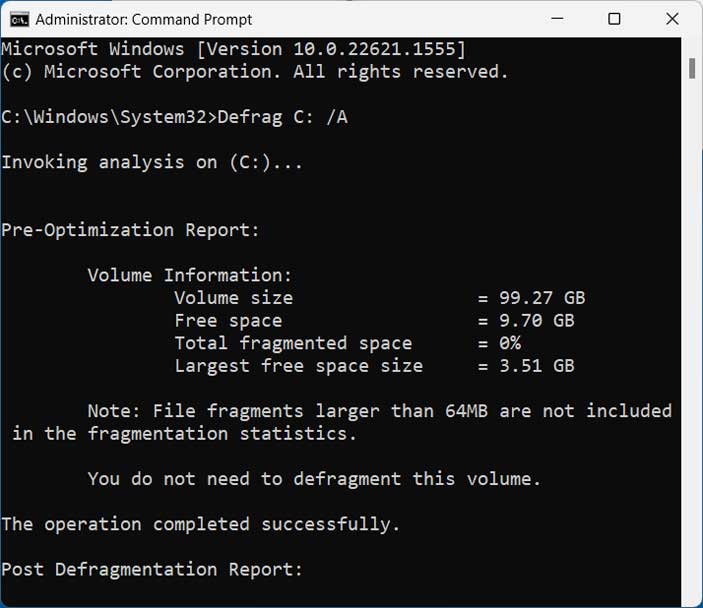
To find out for sure, you can open an administrative command prompt and run a defrag analysis using the Defrag C: /A command (you can change the C to whichever drive letter you are trying to check). If you get a message that says The dirty bit is set on this volume with an error code of 0x89000015, then that is most likely why you are unable to defrag the drive.
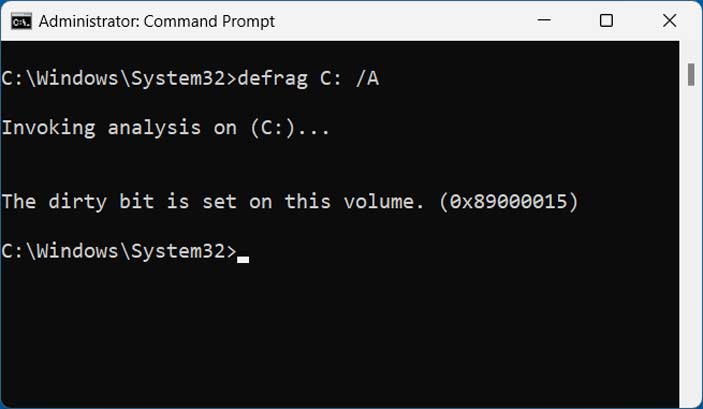
You might get prompted to run a check disk (chkdsk) when the dirty bit is set but often times this will not fix the problem.
One relatively simple way to clear the dirty bit on your drive is to boot your computer using the SystemRecovery Linux based system rescue toolkit which comes with a variety of tools that can be used to troubleshoot and repair your computer.
You can download the SystemRescue ISO file from their website here.
Once you download the ISO file and make a bootable CD or USB drive using software such as Rufus, you can then boot your computer with it to get to the main menu. From there you will want to select the first option that says Boot SystemRescue using default options.
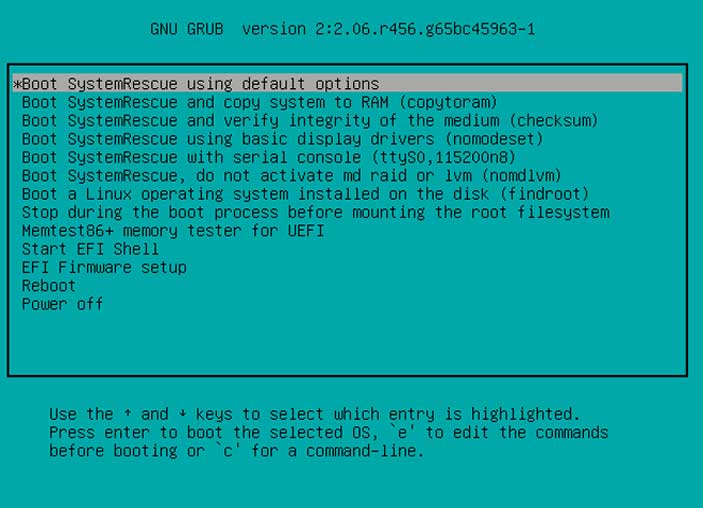
Next you will be presented with a command line interface where you will want to type the following command to show all the drives and their partitions on your computer.
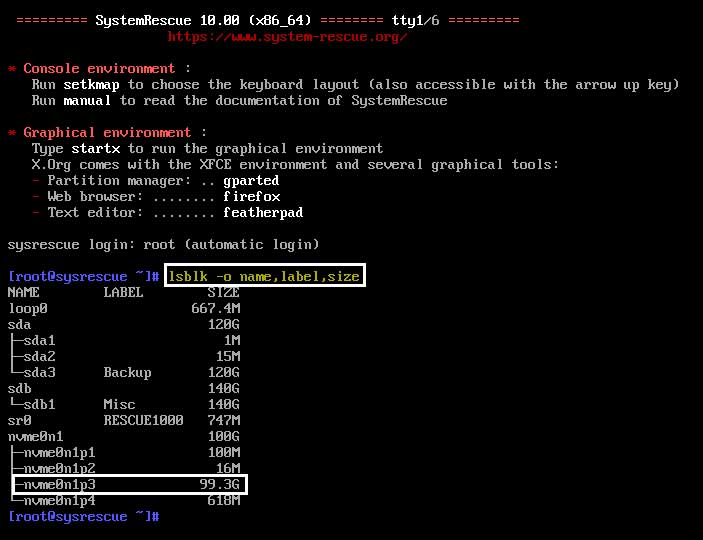
lsblk -o name,label,size
In the example below, there are three hard drives (sda, sdb and nvme0n1). If you have more than one hard drive, be sure to make a note of its size so it will be obvious which one you will need to be working with since this will not show Windows drive letters. Under each drive you will see its partitions such as sda1, sda2 etc. I will be working with the 99.3GB partition labeled nvme0n1p3
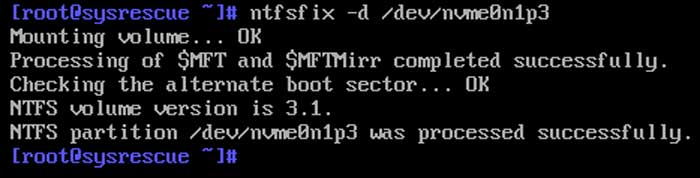
The next command that needs to be run is the nfsfix command with the d switch. After the switch you need to specify the partition so the command will look like the following.
ntfsfix -d /dev/nvme0n1p3.
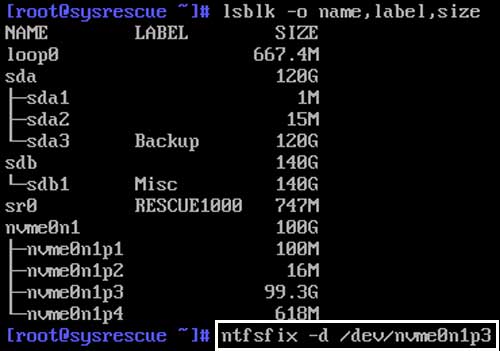
If everything works correctly, you will see a message saying the partition was processed successfully.
You can then type in reboot to have the computer restarted. You might want to remove the SystemRecovery CD or flash drive first to make sure it doesn’t boot to it again.
Now when you are back in Windows, you can open an administrative command prompt and type in Defrag C: /A once again and it should run the analysis this time and not show you the dirty bit message.
You can also go to the properties of the drive and then to the tools > optimize section and check it from there and also run the defrag if needed.
This is how you can reset the hard disk dirty bit in Windows to keep your computer running smoothly.