The Windows command prompt is used to do things such as run programs, change system settings, get system information and run commands to perform various administrative tasks. One example of a commonly used command is the ipconifg command used to get the IP addresses of your computer’s network interfaces.
The command prompt has been around since the days of the Microsoft DOS operating system when there was no Windows graphical user interface (GUI) to work with and everything was done with typed commands. Newer versions of Windows don’t use DOS for a backend but the command prompt can still perform many of the same tasks as a true DOS command line does plus many more.
If you use the command line a lot then you may want to customize its settings or options so that it will be easier for you to use and make your command line activities more productive. To get to the command line properties find your Command Line icon or shortcut and right click it and choose Properties. By default the command prompt shortcut is in Accessories under the start menu.
One of the first things you may want to do is change the starting path for your commands. If you have noticed when you open a command prompt the path is usually set to your user folder.
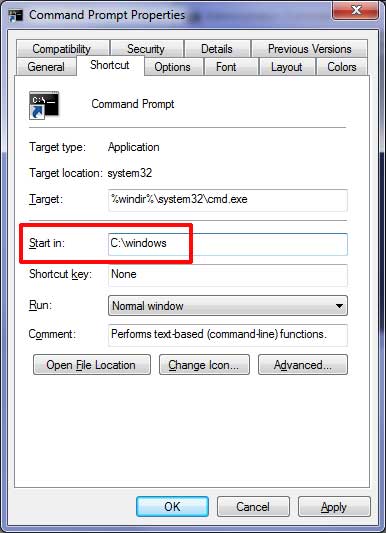
This can be changed by going to the Shortcut tab and then the Start in section. It may currently say something like %HOMEDRIVE%%HOMEPATH% which means that it will read the information for the logged in user and set the path based on that. What you can do is change this path to something else that you use more often when running command such as the root of the C drive or C:Windows.
Now when you open your command prompt you will start in your new default location.
Other things you can do on the Shortcut tab include having the command prompt window open in a normal window or maximized as well as change its default icon. Clicking on Advanced will allow you to have the command prompt run as Administrator each time you open it if you choose to do so.
The Options tab is where you can change things like the cursor size and enable Quick Edit mode which allows you to highlight and copy text within the command prompt window. The Command history setting is where you can change how many previous commands your session will remember. To get to a previous command simply hit the up arrow on the keyboard to bring previous commands back up.
On the Fonts tab you can choose a different font and change the window size. Changing the window size will allow you to fit more text on one row of the screen without it having to wrap to the next line. If you want to create your own custom window size then go to the Layout tab and change the values for the Window size fields.
If you want to use a different color for your background and font besides the default black and white you can do so from the Colors tab. The values you can change here include screen text, screen background, pop-up text and pop-up background.
One thing to keep in mind is that if you change these settings from your command prompt shortcut and then open a command prompt from Start and Run those changed settings won’t apply.